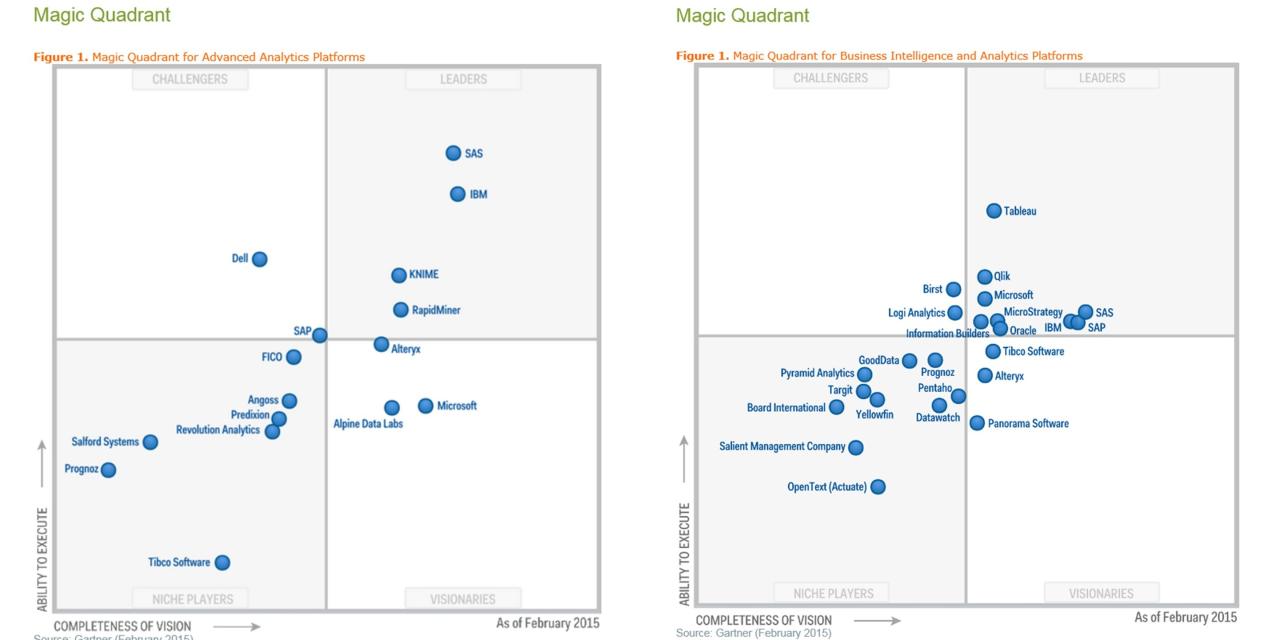
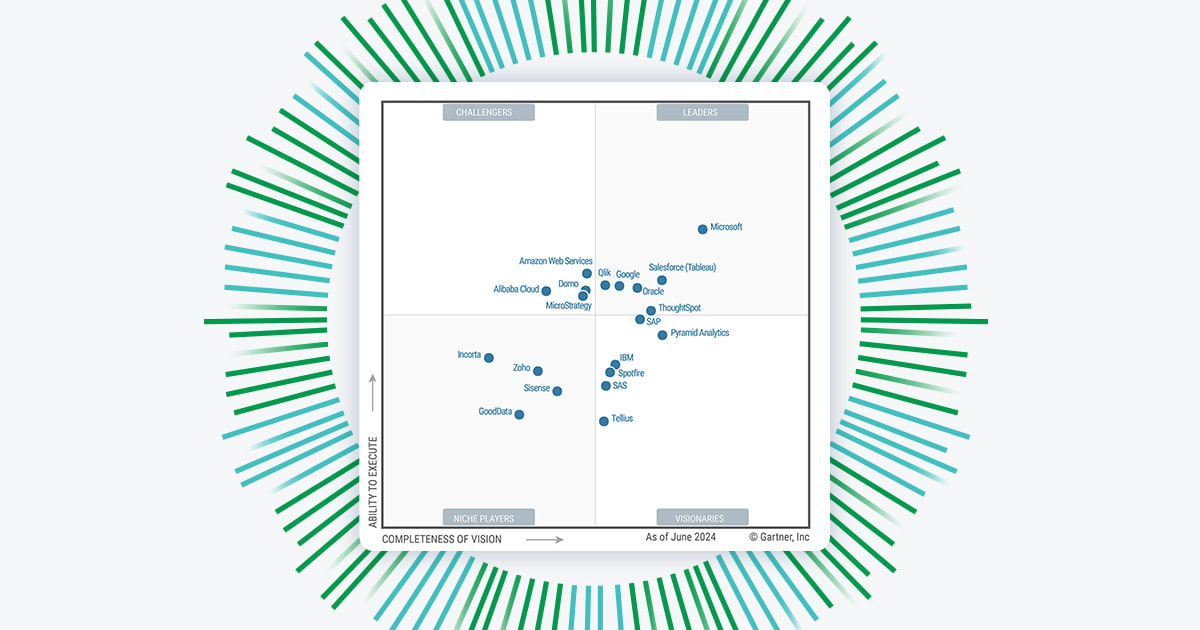
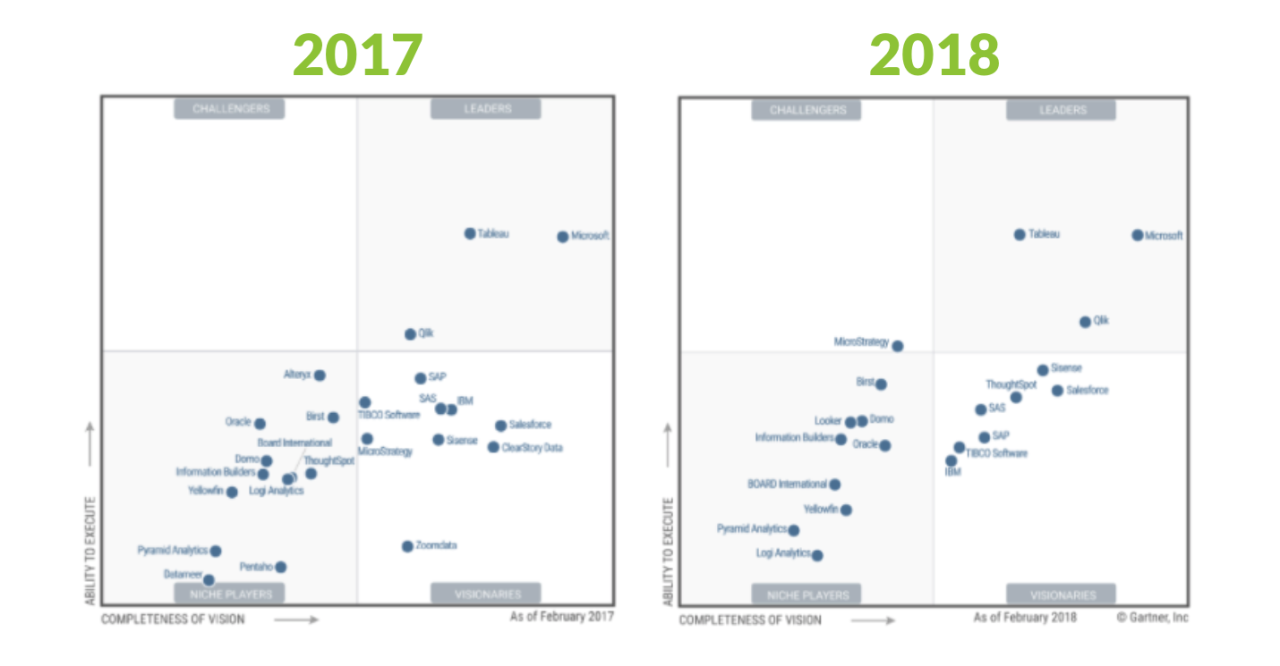
gartner magic quadrant for analytics and business intelligence platforms sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
This framework is crucial for organizations seeking to navigate the complex landscape of analytics and business intelligence tools. It categorizes vendors into four quadrants—Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players—providing insights into their performance, completeness of vision, and ability to execute. By understanding where each vendor stands, businesses can make informed decisions about technology investments that will shape their data strategies.
Technology has always been a driving force behind human progress. From the invention of the wheel to the development of the internet, each leap forward has transformed the way we live, work, and interact with one another. In this article, we will explore the significant milestones in the evolution of technology and how they have shaped our modern world.
1. The Dawn of Civilization
The story of technology begins with the earliest human civilizations. The invention of simple tools, like stone axes and knives, marked the start of a significant shift in human capability. These tools allowed early humans to hunt, gather, and eventually farm, paving the way for permanent settlements and the rise of agriculture around 10,000 BC.
The agricultural revolution was not just about food production; it led to the development of societies and, consequently, new technologies. Innovations such as the plow, irrigation systems, and storage facilities laid the groundwork for future advancements, enabling civilizations to thrive.
2. The Age of Discovery
The next significant leap in technology came during the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries. Advances in navigation and shipbuilding allowed European powers to explore the world, leading to the exchange of ideas, cultures, and technologies across continents. The invention of the compass and the astrolabe were crucial during this era, facilitating long sea voyages that were previously unimaginable.
Additionally, this period saw the introduction of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 1440s. This revolutionary invention democratized knowledge, making books more accessible and fostering a culture of learning and literacy that would ignite the Renaissance.
3. The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution that began in the late 18th century marked another dramatic turning point. The transition from agrarian economies to industrialized ones radically changed society. Innovations such as the steam engine, spinning jenny, and power loom revolutionized manufacturing, allowing for mass production and the rise of factories.
This era not only transformed economies but also had profound social implications. Urbanization surged as people moved to cities in search of work, leading to changes in lifestyle and societal structures. The Industrial Revolution also set the stage for future innovations in transportation, such as railroads and steamships, further connecting the world.
4. The Age of Electronics
The 20th century ushered in the Age of Electronics, characterized by rapid advancements in electrical engineering. The invention of the radio, television, and later, the computer, revolutionized communication and entertainment. These technologies changed how information was disseminated and consumed, shrinking the world even further.
World War II acted as a catalyst for technological advancements, particularly in computing. The development of the first electronic computers, such as ENIAC, laid the groundwork for the modern computing era. Post-war, the rise of personal computers in the 1970s and 1980s brought computing power to the masses, changing the way people interacted with technology.
5. The Digital Revolution
The late 20th and early 21st centuries marked the onset of the Digital Revolution. The advent of the internet fundamentally altered how we communicate, access information, and conduct business. The World Wide Web, created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989, opened up vast possibilities for connectivity and information sharing.
Social media platforms, e-commerce, and mobile technology have transformed human interaction and commerce. People can now connect instantly across the globe, share experiences, and conduct business from the comfort of their homes. This level of connectivity was unimaginable just a few decades ago.
6. Emerging Technologies
As we move further into the 21st century, emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are beginning to shape our lives in unprecedented ways. AI is revolutionizing industries, from healthcare to finance, enhancing efficiency and decision-making processes.
The IoT is making everyday objects smarter, allowing for automation and improved data collection in various sectors. Smart homes, connected cars, and wearable technology are becoming increasingly commonplace, indicating a shift towards a more interconnected and data-driven world.
7. The Future of Technology
Looking ahead, the future of technology holds immense potential but also poses significant challenges. As we continue to innovate, ethical considerations surrounding privacy, security, and the impact of technology on jobs and society must be addressed. The rapid pace of change demands that we adapt quickly while ensuring that technology serves to enhance the human experience.
Moreover, sustainability will play a crucial role in technological development. As we face pressing environmental issues, technologies that promote renewable energy, resource conservation, and sustainable practices will be essential for a balanced future.
Conclusion
The evolution of technology is a testament to human ingenuity and resilience. From ancient tools to advanced digital systems, each leap forward has brought with it new possibilities and challenges. As we stand on the brink of further advancements, it is crucial to reflect on our past, embrace the present, and thoughtfully shape the future of technology for generations to come.
Questions and Answers
What is the gartner magic quadrant?
The gartner magic quadrant is a research methodology that provides a visual representation of a market’s direction, maturity, and participants, categorizing them into four quadrants based on their performance and vision.
How often is the gartner magic quadrant updated?
The gartner magic quadrant is typically updated annually, although some sectors may see more frequent updates depending on market changes and technological advancements.
Who should use the gartner magic quadrant?
Organizations looking for analytics and business intelligence solutions should use the gartner magic quadrant to evaluate vendors, understand market trends, and make informed technology purchasing decisions.
What are the benefits of using the gartner magic quadrant?
It helps organizations quickly identify the strengths and weaknesses of different vendors, assists in comparing options, and provides a clear visual representation of market positioning.
Can the gartner magic quadrant predict future trends?
While it provides insights into current market positioning, it can also hint at future trends based on technological advancements and shifts in vendor strategies.