Delving into magic quadrant business intelligence offers a fascinating glimpse into how organizations can leverage data to drive decision-making and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. This analytical framework not only evaluates various business intelligence solutions but also categorizes them based on their completeness of vision and ability to execute.
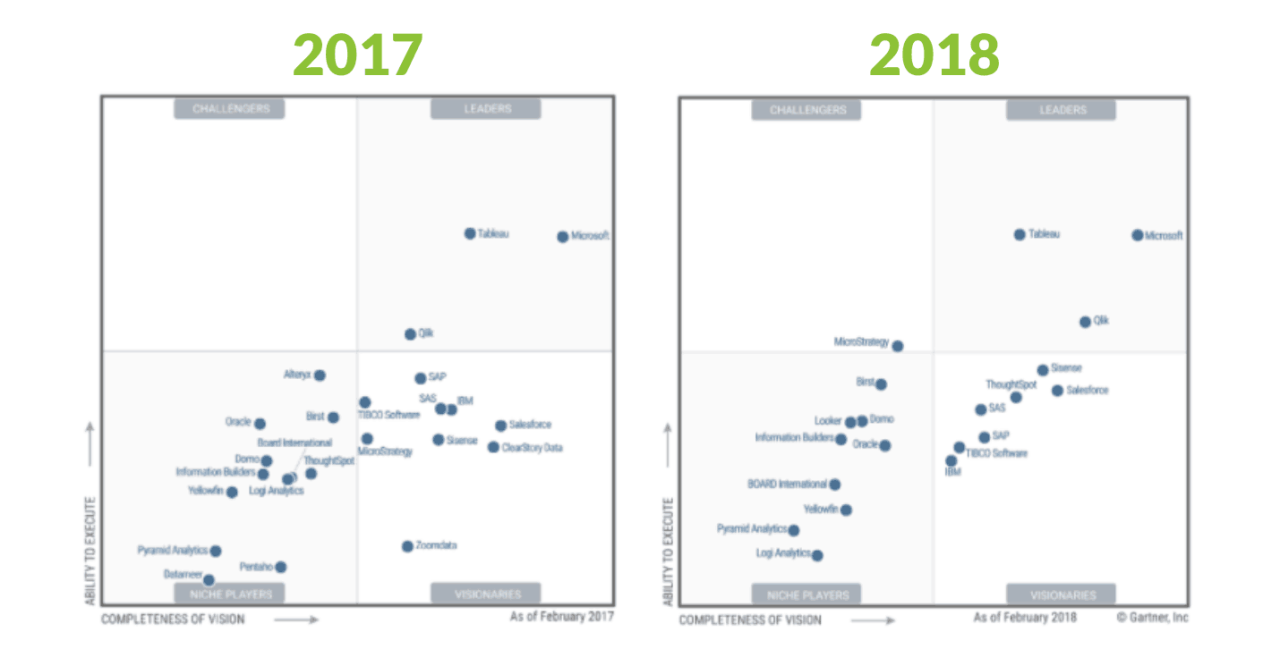
Understanding the magic quadrant is crucial for businesses aiming to navigate the complex landscape of BI tools. It aids companies in identifying the right fit for their unique needs, ensuring they invest in technology that aligns with their strategic goals while optimizing operational efficiency.
Technology has transformed the way we live, communicate, and interact with the world around us. From ancient inventions to modern-day innovations, the journey of technological development is a fascinating narrative that continues to shape our future. In this article, we will explore the key milestones in the evolution of technology, examining how these advancements have influenced society and the way we conduct our daily lives.
Ancient Innovations: The Dawn of Technology
The origins of technology can be traced back to prehistoric times when early humans discovered that they could manipulate their environment to meet their needs. The first significant technological advancement was the creation of tools. Primitive tools made from stone, bone, and wood allowed early humans to hunt, gather, and build shelters. This basic understanding of tool-making laid the foundation for future innovations.
As civilizations began to form, technologies grew more sophisticated. The invention of the wheel around 3500 BC revolutionized transportation and trade, while the development of writing systems in Mesopotamia around 3000 BC enabled the recording of information and facilitated communication. These early advancements were pivotal, marking the transition from nomadic lifestyles to settled communities and commerce.
The Agricultural Revolution: Cultivating Change
Approximately 10,000 years ago, the Agricultural Revolution fundamentally altered human society. The domestication of plants and animals allowed for the establishment of stable food sources, leading to population growth and the development of cities. Technologies such as irrigation systems and plows significantly increased agricultural productivity, providing surplus food that supported growing populations.
This period also saw advancements in metallurgy, with the discovery of copper and bronze smelting processes. These materials were used to create stronger tools and weapons, further enhancing agricultural practices and societal organization. The emergence of trade networks facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas, paving the way for more complex civilizations.
The Classical Era: Philosophical and Scientific Advancements
The Classical Era, spanning from around 500 BC to 500 AD, was marked by significant philosophical and scientific advancements. Greek and Roman scholars made remarkable contributions to mathematics, physics, and engineering. The invention of the aqueduct, for example, showcased the application of engineering principles to solve practical problems, supplying cities with fresh water.
During this time, the development of mechanical devices, such as the water mill and the windmill, illustrated the early use of renewable energy sources. These innovations laid the groundwork for later technological developments and emphasized the importance of harnessing natural forces for human benefit.
The Middle Ages: A Period of Innovation
The Middle Ages, often referred to as the “Dark Ages,” was a time of significant technological advancement despite the challenges faced by society. The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century revolutionized the spread of knowledge. For the first time, books could be produced on a mass scale, making literature, science, and philosophy accessible to a wider audience.
Additionally, advancements in navigation technology, such as the compass and the astrolabe, facilitated exploration and trade across the globe. This period also saw the development of mechanical clocks, which introduced more precise timekeeping methods, further impacting daily life and societal organization.
The Industrial Revolution: A Technological Explosion
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, marked a significant turning point in technological history. Innovations such as the steam engine, invented by James Watt, transformed industries and transportation. Factories emerged, changing the nature of work and leading to urbanization as people flocked to cities for employment opportunities.
This era also witnessed the development of the telegraph, which revolutionized communication by allowing messages to be sent over long distances with unprecedented speed. The rise of electricity in the late 19th century further propelled technological progress, leading to the invention of electric light bulbs, telephones, and eventually, the radio.
The 20th Century: Technological Integration
The 20th century brought about an unprecedented pace of technological advancement. The invention of the computer in the mid-20th century marked the beginning of the Information Age. Computers evolved from massive machines used in research institutions to personal devices that permeate every aspect of daily life.
The advent of the internet in the late 20th century transformed communication, commerce, and access to information. Social media platforms emerged, changing the way people interact and share information globally. This era also saw advancements in biotechnology, leading to breakthroughs in medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.
The 21st Century: The Age of Connectivity
As we navigate through the 21st century, technology continues to evolve at an astonishing rate. The rise of smartphones and mobile devices has made information accessible at our fingertips. The Internet of Things (IoT) connects everyday objects to the internet, creating smart homes and cities that enhance our quality of life.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing industries, enabling automation and data analysis on a scale previously unimaginable. While these advancements offer incredible opportunities, they also raise ethical questions about privacy, security, and the future of work.
Conclusion: A Future Shaped by Technology
The evolution of technology is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress. Each advancement has built upon the last, shaping society and the way we interact with the world. As we look to the future, it is essential to approach technological development with a sense of responsibility, considering its implications for humanity and the environment.
Understanding the history of technology allows us to appreciate its impact and encourages us to make informed decisions as we continue to innovate. The journey through time reveals that while technology can enhance our lives, it also requires careful consideration and ethical mindfulness to ensure a brighter future for all.
Q&A
What is the magic quadrant in business intelligence?
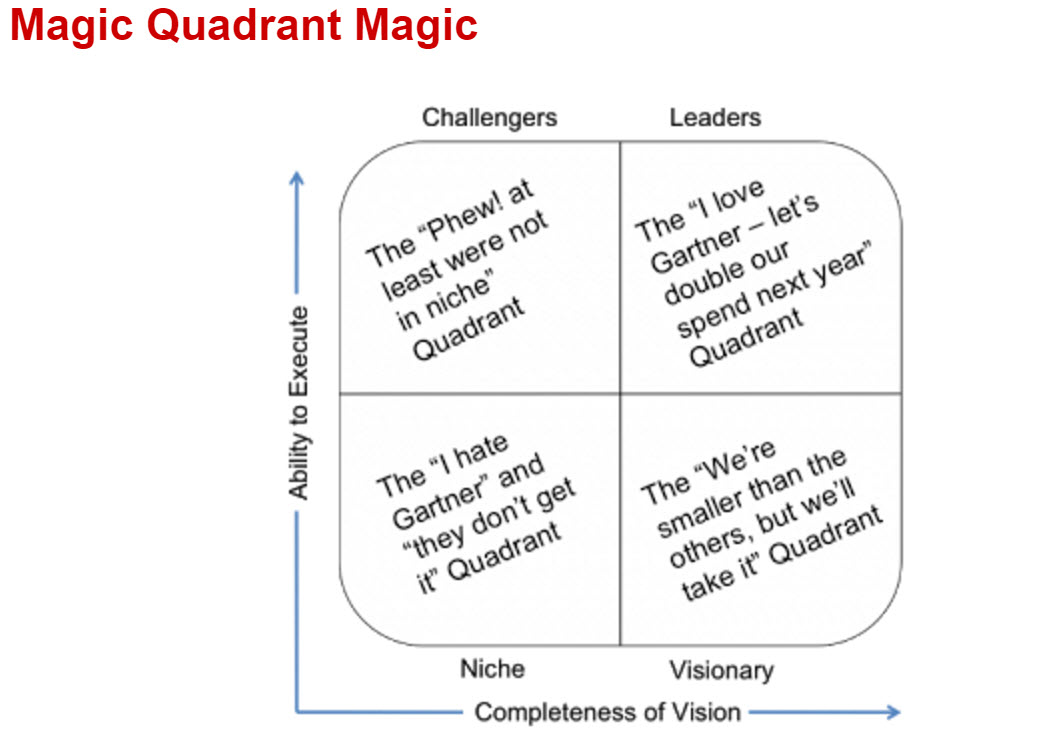
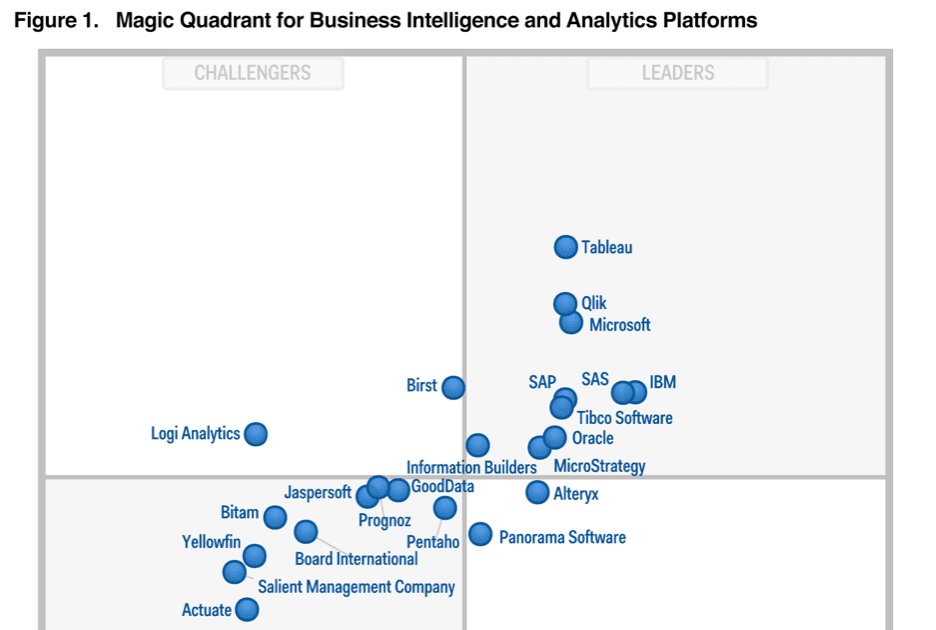
The magic quadrant is a graphical representation that evaluates and categorizes different business intelligence solutions based on their ability to execute and completeness of vision.
How often is the magic quadrant updated?
The magic quadrant is typically updated annually, reflecting changes in the market, technology advancements, and vendor performance.
Who creates the magic quadrant reports?
Magic quadrant reports are produced by research firms, most notably Gartner, which conducts thorough evaluations of vendors in various technology sectors.
Can small businesses benefit from the magic quadrant?
Yes, small businesses can leverage the magic quadrant to identify suitable BI solutions that match their size and specific operational needs.
What are the key factors considered in the magic quadrant?
Key factors include product performance, market presence, customer experience, and the vendor’s vision for future development.