Gartner Decision Intelligence Magic Quadrant offers a compelling look into the evolving landscape of decision-making technologies, allowing organizations to discern the best solutions for their unique needs. As businesses navigate an increasingly complex environment, understanding where different vendors stand in relation to their competitors becomes essential. This framework not only helps decision-makers identify leading technologies but also provides valuable insights into market trends and capabilities.
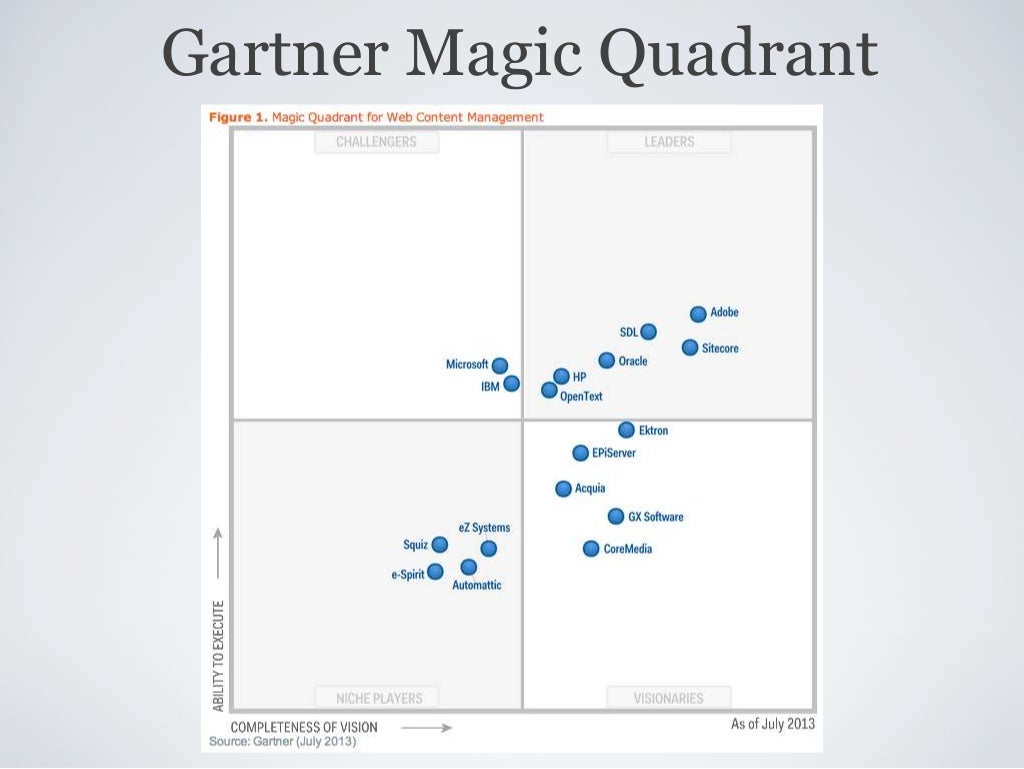
With the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and data analytics, the Magic Quadrant serves as a vital tool for companies aiming to leverage decision intelligence effectively. By categorizing vendors into four distinct quadrants—Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players—Gartner provides a clear visual representation of market positioning, enabling organizations to make informed choices that align with their strategic goals.
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving workplace, technical skills and qualifications alone are no longer sufficient for success. Increasingly, emotional intelligence (EI) has emerged as a crucial factor in achieving professional growth and fostering a positive work environment. But what exactly is emotional intelligence, and why is it so important in the workplace?
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and influence one’s own emotions and the emotions of others. It encompasses five key components: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. These elements work together to shape how we interact with colleagues, handle stress, and navigate the complexities of workplace relationships.
Self-Awareness: The Foundation of EI
Self-awareness is the first step in developing emotional intelligence. It involves recognizing and understanding your own emotions and how they affect your thoughts and behavior. In the workplace, self-aware individuals can identify their strengths and weaknesses, make informed decisions, and communicate effectively with others. They are also more receptive to feedback, which is vital for personal and professional growth.
Self-Regulation: Keeping Emotions in Check
Once you are aware of your emotions, the next step is self-regulation. This means managing your emotions in a way that promotes positive outcomes. For instance, instead of reacting impulsively in a stressful situation, a person with high emotional intelligence will pause, assess the situation, and respond thoughtfully. This ability to control emotions not only enhances personal well-being but also contributes to a more harmonious workplace atmosphere.
Motivation: The Drive to Succeed
Motivation is another vital component of emotional intelligence. It goes beyond external rewards like salary and recognition; it encompasses an intrinsic drive to achieve goals and pursue personal growth. Employees who are motivated by their passion for their work tend to be more engaged, productive, and resilient in the face of challenges. This enthusiasm can be contagious, inspiring colleagues and fostering a culture of excellence within the team.
Empathy: Understanding Others
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. In the workplace, empathy is essential for building strong relationships and maintaining effective communication. Leaders with high empathy can better understand their team members’ needs and concerns, which in turn helps them to provide support and guidance. Practicing empathy not only enhances collaboration but also leads to a more inclusive and supportive work environment.
Social Skills: Building Strong Connections
Finally, social skills are the ability to manage relationships and build networks. This includes effective communication, conflict resolution, and teamwork. Individuals with strong social skills can navigate complex social situations, inspire and influence others, and work collaboratively toward common goals. In a workplace setting, these skills are invaluable for fostering cooperation, enhancing team dynamics, and driving overall organizational success.
The Benefits of Emotional Intelligence in the Workplace
Incorporating emotional intelligence into the workplace yields numerous benefits. Organizations that prioritize EI often experience:
- Improved Communication: Team members with high emotional intelligence communicate more openly and constructively, leading to fewer misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Enhanced Teamwork: With better empathy and social skills, teams can collaborate more effectively, capitalizing on each member’s strengths.
- Increased Employee Engagement: Workplaces that foster emotional intelligence tend to have higher levels of employee engagement, leading to lower turnover rates and higher productivity.
- Better Leadership: Leaders who demonstrate emotional intelligence can inspire and motivate their teams, creating a positive and productive work environment.
- Healthier Work Environment: A focus on emotional intelligence can help reduce workplace stress, promote mental health, and foster a sense of belonging among employees.
How to Develop Emotional Intelligence
Fortunately, emotional intelligence is not a fixed trait; it can be developed over time. Here are some strategies for enhancing your EI:
1. Practice Self-Reflection
Take time to reflect on your emotions and reactions in various situations. Journaling can be a helpful tool for this process, allowing you to track patterns in your emotional responses and identify areas for improvement.
2. Seek Feedback
Ask trusted colleagues for feedback on your emotional responses and interpersonal skills. Be open to constructive criticism and use it as a learning opportunity.
3. Cultivate Empathy
Make a conscious effort to understand others’ perspectives. Engage in active listening and practice putting yourself in others’ shoes, especially during conflicts or challenging conversations.
4. Enhance Your Communication Skills
Work on your verbal and non-verbal communication skills. Effective communication is a key component of emotional intelligence, and being clear and empathetic in your interactions can greatly improve relationships.
5. Manage Stress
Develop coping strategies for managing stress and emotions, such as mindfulness, meditation, or physical exercise. A calm mind is better equipped to handle emotional challenges.
Conclusion
In a world where collaboration and interpersonal relationships are more important than ever, emotional intelligence has become a vital skill set for success in the workplace. By understanding and developing emotional intelligence, individuals can enhance their personal and professional lives, promote a healthier work environment, and contribute to the overall success of their organizations. Embracing EI is not just a personal journey; it’s a collective effort that can lead to transformative changes in the workplace.
Q&A
What is the purpose of the Gartner Magic Quadrant?
Its purpose is to provide a graphical representation of a market’s direction, maturity, and participants, helping organizations evaluate vendors.
How often is the Magic Quadrant updated?
The Gartner Magic Quadrant is typically updated annually, although some sectors may see more frequent updates based on market dynamics.
Can small companies be included in the Magic Quadrant?
Yes, small companies can be included, particularly if they demonstrate unique capabilities or niche solutions that are relevant to the market.
What criteria does Gartner use to evaluate vendors?
Gartner evaluates vendors based on their ability to execute and their completeness of vision, including factors like product performance, customer experience, and market strategy.
Is the Magic Quadrant report free to access?
Access to the full Magic Quadrant report typically requires a subscription or purchase, but summary information may be available for free.